| Size of the INDUSTRY | 88 scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) - 28 public sector banks, 29 private banks and 31 foreign banks. |
| Geographical distribution | Mumbai, Bangalore, Pune, Hyderabad, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata |
| Output per annum | 10% of the share |
Punjab National Bank was established expanding the markets by the 1900s, Bank of India the year in 1895 in Lahore and the same Bank of India 1906, in Mumbai - both were founded under private ownership. Then later in the year 1935, the Reserve Bank of India formally took over the responsibility of regulating Indian banking sector. In the year 1947, after India's independence the Reserve Bank was nationalized and given more powers.

Narasimha Rao government formulated a policy of liberalization in the year 1990 and gave licenses to a small number of private banks, which was known as the New Generation tech-savvy banks, some of the banks were like the UTI Bank(now re-named as Axis Bank) ,ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank. Liberalization along with the rapid growth in the economy of India boosted the banking sector in India, which has seen strong contribution from all the three sectors of banks, namely, government banks, private banks and foreign banks. The next stage for the Indian Banking Industry was to setup with the proposed relaxation in the norms for Foreign Direct Investment, where voting rights were given to all the Foreign Investors in banks which could exceed the present cap of 10%, at present it has gone up to 49% with some restrictions.
Indian Banking Industry was completely shooked with the new policy. Till this time the Bankers used to the follow the 4-6-4 method (Borrow at 4%; Lend at 6%; Go home at 4) of functioning. This new wave ushered in a modern outlook and tech-savvy methods of working for traditional banks which led to the retail boom in India. People not only just demanded more from their banks but also received more. Today Banking in India is generally fair and mature in terms of supply, product range and reach though in rural India still remains a challenge for the private sector and foreign banks. Banking in terms of quality of assets and capital adequacy, banks in India are considered to have clean, strong and transparent balance sheets relative to other banks in comparable other economies. The Reserve Bank of India is the autonomous body, with has the minimal pressure from the government.
The Reserve Bank of India had permitted Warburg Pincus to increase its stake in Kotak Mahindra Bank (a private sector bank) to 10% in March 2006. It is the first time an investor has been allowed to hold more than 5% in a private sector ban. As the RBI announced norms in 2005 that any stake exceeding 5% in the private sector banks.
By the end of March 2010 the total assets of all scheduled commercial bank was estimated at Rs 40,90,000 crores. Which constitutes of about 65 % of GDP at current market prices as compared to 67 %in 2002-03. Banks assets were also expected to grow at an annual composite rate of 13.4 % during the rest of the year against the growth rate of 16.7 % that was between 1994-95 and 2002-03.

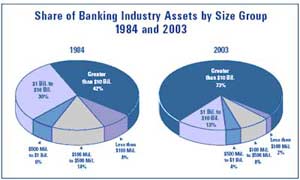
Presently India has 88 scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) - 28 public sector banks, 29 private banks and 31 foreign banks. These banks have a combined network of over 53,000 branches and 17,000 ATMs. According to a report of the Rating Agency ICRA Limited the public sector banks hold over 75% of total assets of the banking industry, with the private and foreign banks holding 18.2% and 6.5% respectively. |
 |
 | The major players in the Indian banking industry are the Bank of Baroda, State Bank of India, Canara Bank, Punjab National Bank, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, HSBC Bank, ABN AMRO Bank, American Express, etc.
|
-
A report of RNCONS by a market research company called "Opportunities in Indian Banking Sector", forecasts that the Indian banking sector will grow at a healthy compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 23.3 per cent till 2011.
-
I The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has provided qualified full banking (QFB) privileges to ICICI for its branch operations in Singapore. Currently, only SBI has the QFB privileges in country.
-
Standard Chartered Bank in India reported a profit of above US$ 1 billion for the first time. The bank had the profit before tax (PAT) of US$ 1.06 billion in the year, 2009 as compared to US$ 891 million in 2008.
-
Punjab National Bank (PNB) has planned to expand its international operations by foraying into Indonesia and South Africa. The bank is planning to increase the share in the international business operations to 7 % in the next three years.
 Recent Press Release
Recent Press Release
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
 INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
INDIAN Bank AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
 Indian Banks' Association (IBA)
Indian Banks' Association (IBA)
Indian Industries
 |
INDIAN INDUSTRIES |


