| Size of the INDUSTRY | It contributes almost 18.5% to India's GDP, while it accounts for about 13% of the country's total exports. |
| Geographical distribution | All over the country |
| Output per annum | According to the analysts the turnover of the total food market is approximately Rs.250000 crores out of which value-added food products comprises of Rs.80000 crores. |
| Market Capitalization | During 1990-91, the contribution of agriculture to the country's GDP output was at 32%, which was decreased to 20% by 2005-06. |

The British rule in India witnessed the destruction of century-old water management structures and a virtual wreckage of the knowledge systems and cultural traditions that had helped build and preserve these water-management techniques over the centuries in states such as Bihar, Bengal, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and others. Indian had a stagnant performance of agriculture in during the colonial period which turned into a sustained growth since 1947, then with a stronger performance in India especially in terms of per-capita food production the Indian Agricultural Industry grew.
After Independence the early years witnessed accentuation (emphasis) on the development of infrastructure for scientific agriculture. The Important steps were like including the establishment of fertilizer, pesticide factories, construction of large multi-purpose irrigation-cum-power projects, organization of community development projects and national extension programmes and even most majorly starting the agricultural universities as well as new agricultural research institutions across the length and breadth of the nation.

This Indian Agricultural Industry revolution brings along with it the opportunities of profitable investment. The Indian government initiative has taken up to improve the Agricultural Standards by formulating the policies like EXIM policy, price policy, seed policy and this has paved the way for the profits to the Agricultural Industry in India. The statistics convey that the Indian Agricultural Industry today is the world's second largest producer of food. From canned, dairy, processed, frozen food to fisheries, meat, poultry, food grains, alcoholic beverages & soft drinks, the Indian agro industry has dainty areas to choose for business.
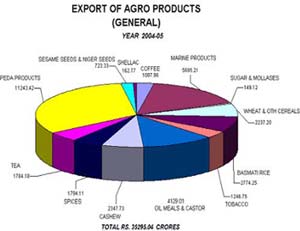
Indian Agricultural industry also assumes significance owing to India's sizable agrarian economy, which contributes over 35% of GDP and employs around 65 % of the population. The consumer food segment goods have top priority both in terms of foreign investment and number of joint- ventures / foreign collaborations. Indian agricultural industry that have the capacity to lure foreigners with promising benefits are the deep sea fishing, aqua culture, milk and milk products, meat and poultry segments.

• Rallis
• H. J. Heinz
• Advanta India Ltd.
• Phalada Agro Research Foundation Ltd.
• Poabs Organic Estates
• National Agro Industries
• DuPont India
• Rasi Seeds
• ABT Industries
Work in agricultural sectors ranges from the academic pursuits of research and teaching to inspection, supervisory work and to other commercial activities of establishing farms, plantations, orchards and carrying on exports of produce from them. Basic training in agriculture is offered for Bachelor's degree course of three to four years duration at all the agricultural universities in the country. For graduate level courses candidates can take admission directly at any state agricultural university. The eligibility criterion for an individual would be 12th pass in science / agriculture. Many universities fix a minimum aggregate of 50% marks to be obtained in the qualifying examination.
• As a consequence to the development initiatives taken up by the Indian government, many large Indian conglomerates are investing in agribusiness through by the way of agro-exports, processing, organized retailing and marketing. In recent years agricultural sector has evidenced frantic activity because of huge investments by companies such as ITC, Bharati's Field Fresh, Reliance Industries Limited, PepsiCo, M&M's Mahindra Shubhlabh, and Aditya Birla Group among others.
• For Ensuring product quality and safety -A big challenge is faced by these Indian agro-industries is to ensure the availability of quantity and satisfactory quality of raw materials in order to meet the demands of processing, export and retail markets. Modern value chains are developed by these companies that are emerging alongside the traditional value chains to meet their specific quantity and quality requirements. Many research organizations have documented case studies of successful examples of modern supply chains where smallholder farmers in India are involved in meeting international quality standards. These draft case studies compare these farmers involved in modern value chains with their counterparts in the traditional markets from the perspective of farmer prices, risk management, access to inputs and production technology.
 Recent Press Release
Recent Press Release
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
 INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
INDIAN AGRICULTURAL AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
 Process Plant & Machinery Association of India (PPMAI)
Process Plant & Machinery Association of India (PPMAI)
 Indian Agricultural Association(IAA)
Indian Agricultural Association(IAA)
Indian Industries
 |
INDIAN INDUSTRIES |


