| Size of the INDUSTRY | The total capacity is spread over 129 plants, which is owned by 54 major companies across the country. |
| Geographical distribution | Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Chennai, Pune, New Delhi, Bangalore, Kolkata, Delhi, Rajkot, Coimbatore, Vadodara, Ghaziabad, Nagpur, Faridabad, Jaipur, Surat, Aurangabad, Indore, Gurgaon, Jodhpur, Thane, Noida, Secunderabad, Thiruchirapalli, Navi Mumbai, Ludhiana, Guwahati, Nashik , Patna , Bhilai, Raipur , Howrah, Siliguri, Kota, Bhubaneswar, Madurai, Ankleshwar, Vapi, Chandigarh, Jamshedpur, Morbi, Udaipur , Bhavnagar, Kanpur, Lucknow, Tuticorin, Vijayawada, Beawar, Goa |
| Output per annum | 217.80 million tonnes |
| Percentage in world market | 8% of share |

A quota of 66.60% was imposed for sales to Government and small real estate developers. Lower quota at 50% was effected for new units and sick units. The remaining 33.40% was allowed to be sold in the open market. These changes had the desirable effects on the Indian Cement industry. Profitability of the manufacturers increased substantially, but such rising input cost was a cause for concern. Complete freedom to the cement industry was given in the year 1989, to gear it up to meet the challenges of free market competition due to the impending policy of liberalization. In 1991 the industry was de- licensed which resulted in an accelerated growth for the industry and availability of state of the art technology for modernization. Major players invested heavily for capacity expansion and the industry laid greater focus on exports to maximize the opportunity available in the form of global markets. The role of the government has been extremely crucial in the growth of the industry.

In spite of it being second largest cement producer in the world, Indian Cement industry falls in the list of lowest per capita consumption of cement with 125 kg. The reason for this is poor rural people who mostly live in mud huts and cannot afford to have the commodity. The demand and supply of cement in India has grown up over the years. In a fast developing economy as India there is always large possibility of expansion of cement industry. The Indian cement industry is one of the vital industries for economic development. The total utilization of cement in a year is used as an indicator of economic growth. Cement contributes as a necessary constituent of infrastructure development and a key raw material for the construction industry, especially in the government's infrastructure development plans in the context of the nation's socio-economic development.
Actual Indian cement production in 2002-03 was 116.35 million tonnes as against a production of 106.90 million tonnes in 2001-02, registering a growth rate of 8.84%. Keeping in view the trend of growth of the industry in previous years, a production target of 126 million tonnes has been fixed for the year 2003-04. During the period April-June 2003, a production (provisional) was 31.30 million ton es. The industry has achieved a growth rate of 4.86 per cent during this period.
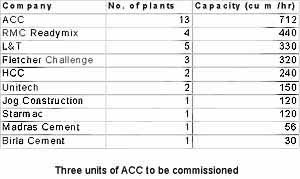 |
|
- The Indian cement industry is expected to grow steadily in 2010-2011 and increase capacity by another 50 million tons in spite of the recession and decrease in demand from the housing sector.
- The industry experts project the sector to grow by 9 to 10% for the current financial year provided India's GDP grows at 7%. India ranks second in cement production after China.
- The major companies have made investments to increase the production capacity in the past few months, heralding a positive outlook for the industry.
- The housing sector accounts for 50% of the demand for cement and this trend is expected to continue in the near future.
The Indian Cement Industry with Modernization and technology up-gradation has become a continuous process for industry. At present international standards and benchmarks in the quality of cement and building materials produced are met in India and is able to compete international markets. Substantial technological improvements have been bought in the industry for which we can legitimately be proud of its state-of-the-art technology and processes incorporated in most of its cement plants. This particular technology up gradation is resulting in increased capacity, reduction in cost of production of cement. In 2003, a Cris Infac study mentioned that the cement industry could had the capacity addition of approximately 50 MT by 2008, of which Greenfield expansions would contribute 40 MT while debottlenecking of the plants and increase in blending ratios would add another 10 MT, taking the total capacity of the cement industry to around 180 MT.
 Recent Press Release
Recent Press Release
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2021 - 2022
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2020 - 2021
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2019 - 2020
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2018 - 2019
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2017 - 2018
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2016 - 2017
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2015 - 2016
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2014 - 2015
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2013 - 2014
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2012 - 2013
 INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
INDIAN cement industry AT A Glance IN 2011 - 2012
 Cement Manufacturers' Association (CMA)
Cement Manufacturers' Association (CMA)
 |
INDIAN INDUSTRIES |


